Abstract
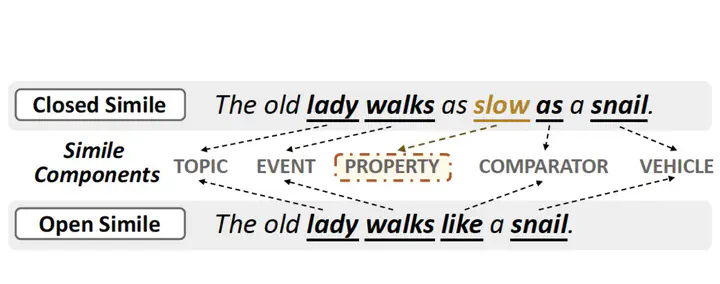
Simile interpretation is a crucial task in natural language processing. Nowadays, pre-trained language models (PLMs) have achieved state-of-the-art performance on many tasks. However, it remains under-explored whether PLMs can interpret similes or not. In this paper, we investigate the ability of PLMs in simile interpretation by designing a novel task named Simile Property Probing, i.e., to let the PLMs infer the shared properties of similes. We construct our simile property probing datasets from both general textual corpora and human-designed questions, containing 1,633 examples covering seven main categories. Our empirical study based on the constructed datasets shows that PLMs can infer similes’ shared properties while still underperforming humans. To bridge the gap with human performance, we additionally design a knowledge-enhanced training objective by incorporating the simile knowledge into PLMs via knowledge embedding methods. Our method results in a gain of 8.58% in the probing task and 1.37% in the downstream task of sentiment classification.